SMART Grid for Requirement Quality
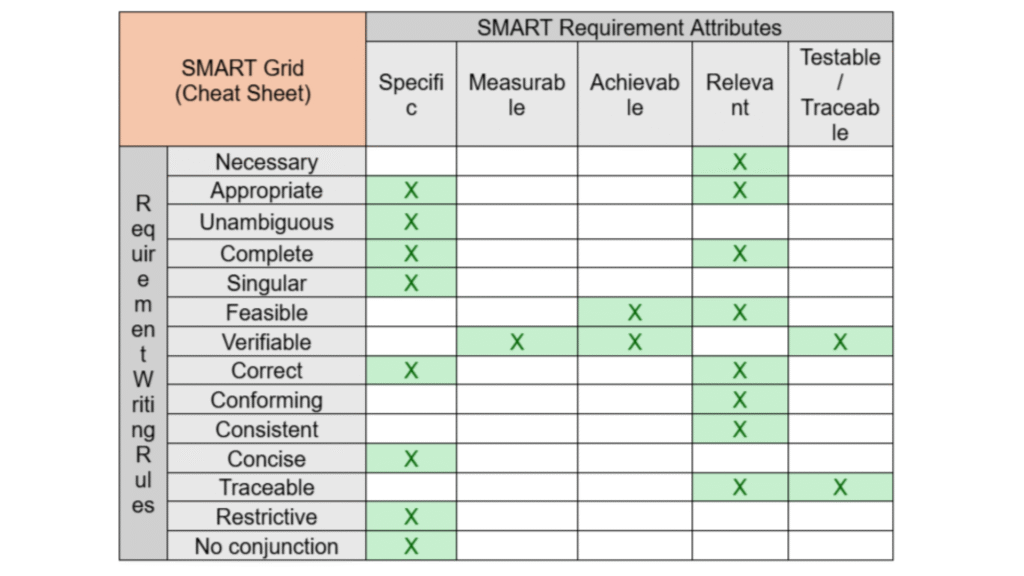
Key Insights from the Grid
- ● Specific: Attributes like Unambiguous, Singular, Concise, Restrictive, and No conjunction
ensure that requirements are written with precision and clarity. Specificity prevents
misinterpretation and sets a solid baseline for design and testing. - ● Measurable: Measurement underpins Verifiable requirements. If a requirement cannot be
quantified or checked against a defined criterion, it cannot be verified effectively. - ● Achievable: Attributes such as Feasible and Verifiable link to achievability. Requirements must
be realistic within project constraints (technology, cost, and schedule). - ● Relevant: Relevance connects to attributes like Necessary, Appropriate, Complete, Correct,
Conforming, and Consistent. A requirement should always contribute directly to the system’s
purpose and higher-level objectives. - ● Testable/Traceable: Verifiable and Traceable requirements depend on the ability to confirm
fulfillment through test, analysis, inspection, or demonstration, and to maintain linkage to
higher-level needs.
Why the SMART Grid Matters
The SMART Grid acts as a quality checklist for engineering requirements. It ensures that requirements are not just written, but written well — minimizing ambiguity, maximizing clarity, and aligning with project goals. Using this structured approach helps teams validate that they are building the right product (validation) and verify that they are building the product right (verification).
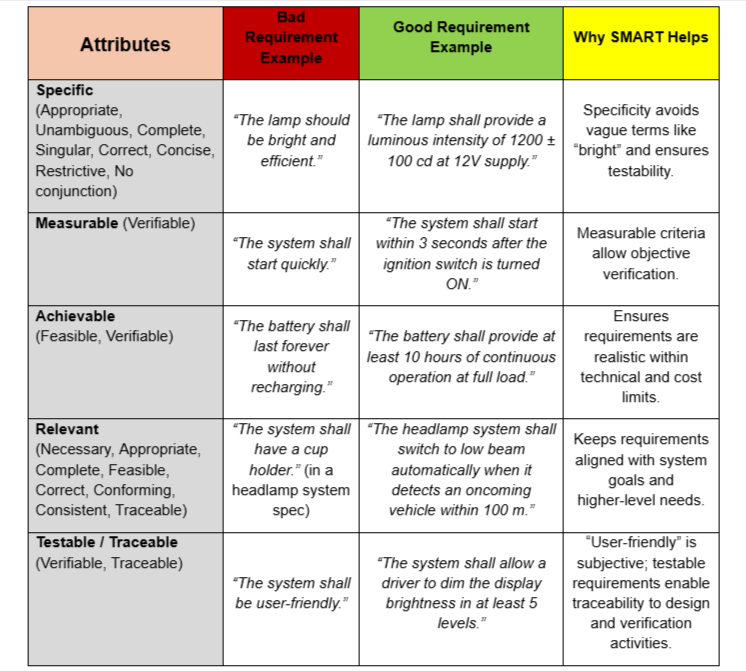
Why the SMART Grid Matters – With Examples
This SMART Grid links requirement quality attributes to SMART principles with good and bad examples as shown in below table. It serves as a quick reference checklist to ensure -requirements are clear, feasible, measurable, and testable.
If you are interested in understanding how to adopt systems engineering and model based systems engineering practices within your organization, reach out to BlueKei Solutions team at info@Blue-Kei.com. We specialize in systems engineering consulting, project executions, process adoptions such as compliance to ISO15288, ARP 4754A, ISO 42020, digital transformations. We can also conduct capability development workshops which are experiential and tailored to your needs. With systems engineering adoption you can address the complexity, manage evolving risks and bring transformation in communication within your organization through digitalization and create the digital thread.

